Results
Neurocognitively-guided modelling of virtual humans for enhanced realism in immersive media
To investigate how human perception differs between real and AI-generated faces, we designed an EEG experiment measuring neurophysiological responses to synthetic images created by Generative Adversarial Networks. We propose to compare these brain signals with standard visual quality metrics like Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) to understand what makes virtual faces appear realistic to human observers. This experimental framework, presented at the neurology department retreat, aims to integrate neurophysiological feedback into deepfake detection and generation systems, creating more human-aligned approaches that better reflect actual human perception of realism in immersive media.
Human-aligned deep and sparse encoding models of dynamic 3D face similarity perception

To test the effect of space and time on face similarity judgments, we conducted a large online experiment in a static 2D and a dynamic 3D condition. We trained computational encoding models of human similarity judgments to investigate the latent representations that underlie their predictions. We found a consistent processing of face similarity between 2D and 3D. However, our encoding models also revealed subtle differences. Our openly available data and models lay the groundwork for understanding our ability to recognize and identify faces in a dynamically changing real world.
Key publication
Hofmann, S. M., Ciston, A., Koushik, A., Klotzsche, F., Hebart, M. N., Müller, K.-R., Villringer, A., Scherf, N., Hilsmann, A., Nikulin, V. V., & Gaebler, M. (2024).
Human-aligned deep and sparse encoding models of dynamic 3D face similarity perception. PsyArXiv.
Source
Real or fake? Decoding realness levels of stylized face images with EEG

We utilized an EEG dataset in which participants were presented with human face images of different stylization levels. We found a non-linear relationship between amplitudes of neural responses and stylization level. Moreover, we successfully decoded the level of realness from the single-trial EEG data. This study provides a basis for future research and neuronal benchmarking of real-time detection of face realness regarding three aspects: SSVEP-based neural markers, efficient classification methods, and low-level stimulus confounders.
Key publication
Chen, Y., Stephani, T., Bagdasarian, M. T., Hilsman, A., Eisert, P. , Villringer, A., Bosse, S., Gaebler, M., Nikulin, V. V. (2023).
Real or fake? Decoding realness levels of stylized face images with EEG. Research Square.
Source
Fooling State-of-the-Art Deepfake Detection with High-Quality Deepfakes

This paper emphasizes the need for robust deepfake detectors in the face of increasing security and privacy concerns. We propose a novel autoencoder and face blending technique to generate high-quality deepfakes, which we use to fool a State-of-the-Art deepfake detector. The results highlight the importance of including high-quality fakes in the training datasets of deepfake detectors for improved generalization and detection of manipulations in real-world scenarios.
Key publication
Beckmann, A., Hilsmann, A., Eisert, P. (2023).
Fooling State-of-the-Art Deepfake Detection with High-Quality Deepfakes. arXiv.
Source
Decoding subjective emotional arousal from EEG during an immersive virtual reality experience
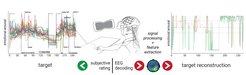
We successfully decoded self-reported emotional arousal during an immersive VR experience involving virtual rollercoasters from EEG-derived parieto-occipital alpha power (Hofmann, Klotzsche, Mariola et al., 2021).
Key publication
Hofmann, S. M., Klotzsche, F., Mariola, A., Nikulin, V., Villringer, A., & Gaebler, M. (2021).
Decoding subjective emotional arousal from EEG during an immersive virtual reality experience. eLife.
Source press release | eLife digest | twitter thread




